In the early stage of oil field exploitation, the oil reservoir often has a large amount of energy, and the oil can flow from underground to the ground by energy. As the energy of the oil reservoir is continuously consumed, when the energy of the oil reservoir is not enough to make the oil flow to the ground along the wellbore by its own energy, it is necessary to supplement the energy artificially to make the oil be extracted to the ground, which we collectively call artificial lift.
This article will introduce the API subsurface rod pump system in the artificial lift method, as well as the structural composition, working principle, typical application scenarios, installation method, and technical differences with other rodless pump systems (such as electric submersible pumps, screw pumps, etc.).
What is artificial lift?
Artificial lift is an oil production technology that replenishes energy to the bottom of the well by artificial means, so that the reservoir fluid can overcome resistance and be transported from the bottom of the well to the ground.
When the oil well enters the late stage of self-flowing, or the natural energy is not enough to start production, an artificial lift device must be installed to maintain the production capacity of the oil well. By changing the pressure relationship of the bottom hole fluid, the artificial lift system enables the reservoir to maintain stable output.
What is API subsurface rod pump?
API subsurface rod pump is a common downhole equipment, driven by a pumping unit to pump crude oil from the well to the ground. Ordinary rod pumps are mainly composed of four parts: pump barrel, suction valve, piston and discharge valve. According to the way the rod pump is fixed underground, it can be divided into tube pump and rod pump.
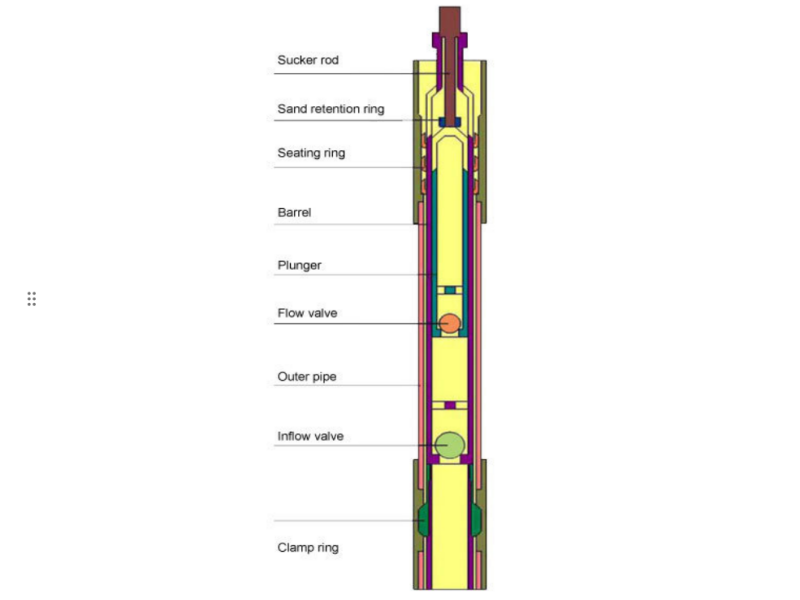
API subsurface rod pump system composition:
1. Ground drive equipment (pumping unit):
The pumping unit is the core device on the ground, usually a balanced walking beam pumping unit or a double horseshoe pumping unit. The motor drives the eccentric wheel, which drives the crossbeam up and down through the connecting rod mechanism, thereby driving the pump rod to reciprocate up and down.
2. Pumping rod column system:
The pumping rod is a group of steel rods connected, which runs through the wellbore from the wellhead to the pump body plunger to transmit power. The rod column is usually equipped with accessories such as centralizers and anti-dropping clamps to ensure that the center position is centered and reduce wear.
3. Downhole pump body (API subsurface rod pump):
The downhole pump body is divided into two parts: the pump barrel and the plunger. The plunger is installed in the pump barrel and completes the suction and discharge of liquid through up and down strokes. There are two types of pumps: tubular pumps and API subsurface rod pumps. Common models are classified according to API standards.
Working principle of API subsurface rod pump:
During the upstroke: the plunger moves up, low pressure is formed in the pump barrel, the fixed valve opens, and the liquid enters the pump chamber.
During the downstroke: the plunger moves down, the fixed valve closes, the liquid is pressed into the oil pipe and discharged to the ground.
Through continuous reciprocating motion, the continuous lifting of the downhole liquid is achieved.
Advantages and applicable scenarios of API subsurface rod pump system:
Advantages and characteristics: simple structure and stable operation. Mature maintenance technology and low operation and maintenance cost. Adapt to a wide range of well depths (shallow wells, medium and deep wells). Applicable to oil wells with medium and low production and less sand content.
Applicable scenarios of API subsurface rod pump:
After the end of self-flowing and the stage of production decline.
Old wells with moderate water content and stable liquid production.
Remote or economic development blocks such as coalbed methane wells and heavy oil wells.
Vertical wells with small well inclination (<10°) where ground space is allowed.
API subsurface rod pump vs. other artificial lift methods:
| Technology type | Advantages | Limitations |
| Rod pump | Low cost, easy maintenance, wide adaptability | Risk of eccentric wear of rod and pipe, poor adaptability to inclined wells |
| Electric submersible pump | Large displacement, high automation, low noise | High initial investment, easy aging of cables, complex downhole system |
| Surface driven screw pump | Simple structure, no cables, strong adaptability | Heavy rod column, restrictions on well depth and viscosity |
| Submersible motor screw pump | Silent, good adaptability to inclined wells | High cost, difficult pump inspection, high requirements for electronic control |
| Air lift/hydraulic jet pump | No moving parts, suitable for deep wells | High energy consumption, low efficiency, inflexible adjustment |
Installation steps: ① Install the pumping unit and electronic control system. ② Lower the sucker rod and downhole pump body. ③ Debug the pump efficiency and stroke matching.
For specific API subsurface rod pump downhole steps, please click to visit the article "Safety Tips for Sucker Rod Pumps from Storage to Downhole"!

