06-09/2025
1. Oil well (pump inspection) operation:
The methods of extracting oil from the formation can be divided into two categories: one is to use the energy of the formation itself to lift crude oil, which is called self-flowing oil production; the other is that due to the lack of energy in the formation itself, it is necessary to artificially use mechanical equipment to supplement the energy of the liquid in the well in order to lift the crude oil to the ground, which is called artificial lifting oil production or mechanical oil production. At present, the main artificial lifting methods in oil fields are gas lift, insert rod pump oil production and rodless pump oil production.
insert rod pump oil production includes pumping unit insert rod pump and ground driven screw pump (generally not used). Rodless pump oil production includes electric submersible pumps, hydraulic piston pumps, jet pumps, etc. Regardless of the lifting oil production method used, due to adjustments to the oil field development plan, equipment failures, etc., pump inspection (replacement) operations are required.
2.Check (replace) the insert rod pump:
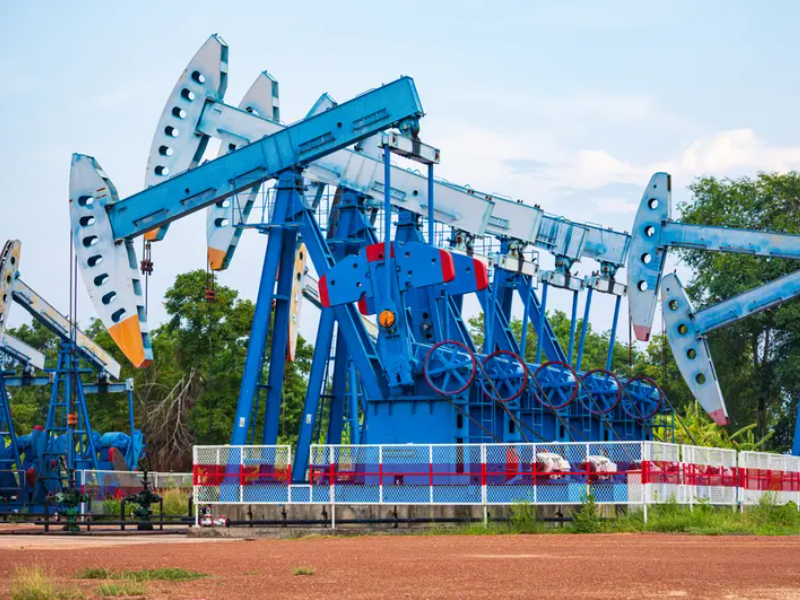
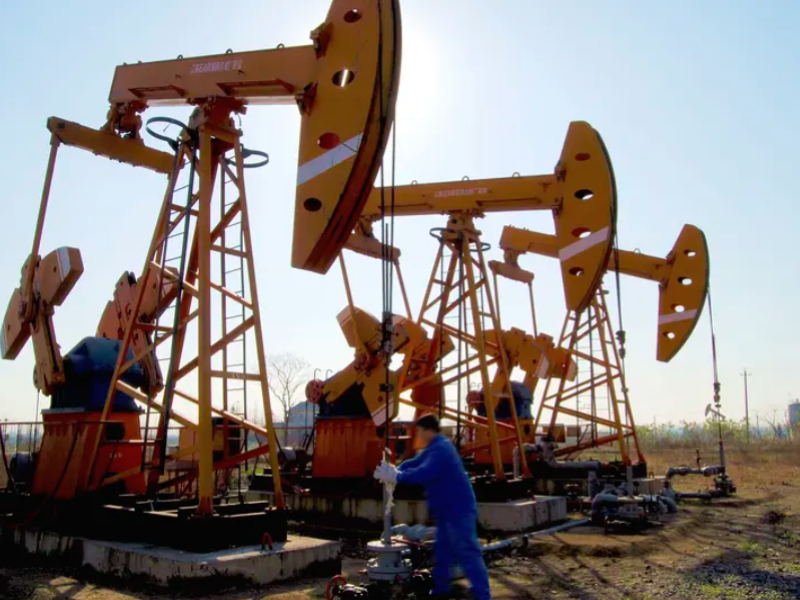
The insert rod pump is a method of producing oil by transferring the reciprocating motion of the pumping unit suspension point to the pumping pump through the sucker rod, and the insert rod pump piston moves up and down to take out the liquid in the well. insert rod pump is currently the most widely used artificial lift oil production method in various oil fields, accounting for about 90% of the number of artificial lift wells. The insert rod pump is mainly composed of a pumping unit, a pumping pump, a sucker rod and supporting tools.
The pump should be inspected due to a failure of the insert rod pump downhole. The time interval between two pump inspections is called the pump inspection cycle. Many factors such as the production of the oil well, the oil layer pressure, the oil layer temperature, the gas and water discharge, the sand and wax deposition of the oil well, the corrosiveness of the crude oil, and the management system of the oil well will affect the length of the pump inspection cycle.