In the previous article, we discussed the RHA Insert Rod Pump. This article will explain the definition, model description, technical specifications, structural components, operating principle, application scenarios, comparison with other pump types, and installation methods of the TH tubing pump.
Table of Contents
What is a TH tubing pump?
TH tubing pump model description
Differences between TH tubing pump and other pump types
Structural components
How to choose the right pump type
Advantages and applicable scenarios
TH tubing pump installation methods
Technical specifications
1. What is a TH tubing pump?
TH tubing pumps are the most widely used type of API standard sucker rod pumps. Unlike API insert pumps, TH tubing pumps are integral pumps that are lowered into the well along with the tubing. This design ensures enhanced sealing performance and greater displacement, making them ideal for deep wells, high production rates, or high downhole pressures.
Their most significant feature is the integrated pump barrel and tubing. Therefore, maintenance requires the entire tubing to be removed. While this comes at a relatively high cost, TH pumps offer excellent mechanical strength and long-term stable operation.
2. TH Tubing Pump Model Description:
TH stands for:
T → Tubing Pump.
H → Heavy-wall, suitable for deep wells, highly abrasive, and high-pressure conditions.
Thus, TH pumps are thick-wall tubing pumps, offering enhanced wear resistance and adaptability.
3. Differences Between TH Tubing Pump and Different Pump Types:
Model Mounting Method Features Applicable Applications
THD Mechanical Anchoring High stability, vibration resistance, and durability. Suitable for deep wells, high-pressure wells, and long-term operation.
THM Mechanical Slips Simple structure, easy installation, and easy replacement. Suitable for medium and shallow wells and complex well conditions.
THC Rubber Seat Seal Excellent sealing and adaptability, requiring regular rubber replacement. Suitable for high-temperature wells, wells containing sand, and wells requiring frequent maintenance.
THB Bottom Anchoring Stable pump body to prevent uneven wear and loosening. Suitable for deep wells, high-yield wells, and those requiring high stability.
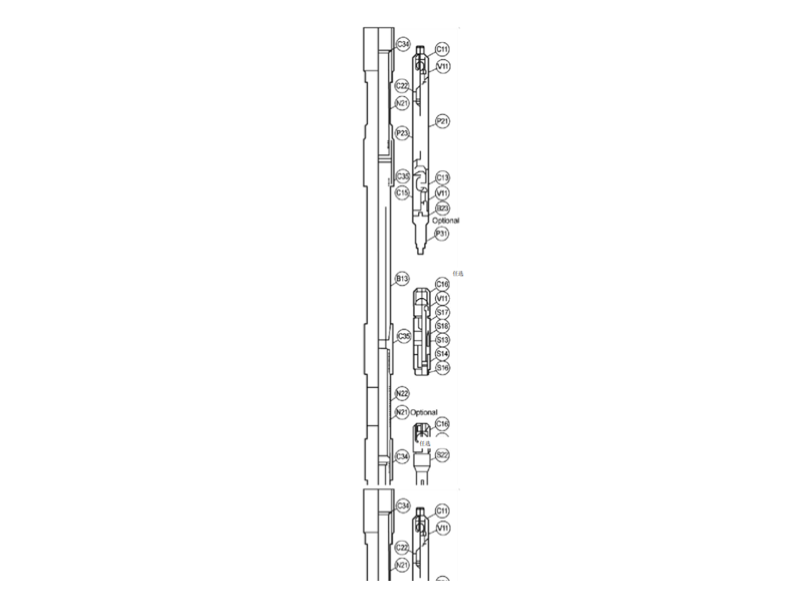
4. Structural Components:
A typical TH tubing pump consists of:
Pump Barrel → Made of high-strength alloy steel or nickel-based material, it is wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant.
Plunger → Reciprocates up and down in the pump barrel to pump liquid.
Valve Assembly → Consists of a fixed valve (intake valve) and a traveling valve (discharge valve), ensuring unidirectional flow.
Tubing Connector → Connects the pump to the tubing.
Auxiliary Components → Seals, valve balls, valve seats, cage, etc.
5. How to Choose the Right Th Tubing Pump Model?
When selecting a TH series tubing pump, consider a comprehensive range of factors, including well depth, production rate, downhole fluid, and ease of maintenance. The following points can be used as a guide:
Based on Well Depth and Pressure:
Deep/High-Pressure Wells → Recommend the THD (Mechanical Anchor) or THB (Bottom Anchor) models for excellent stability and high pressure resistance.
Shallow/Medium-Shallow Wells → Recommend the THM (Mechanical Slip) models for a simpler structure and easier installation.
Based on Downhole Fluid:
High-Temperature Wells/Sand-Containing Wells/High-Impact Wells → Recommend the THC (Rubber Seat Seal) for enhanced sealing and adaptability to wellbore conditions.
Corrosive/Abrasive Fluids → Recommend the THD or THB models, featuring thicker barrels for wear and corrosion resistance.
Based on Maintenance Frequency:
Wells requiring frequent maintenance → Recommend the THC (Rubber Seat Seal) for easy assembly and disassembly, suitable for short-term maintenance. For wells requiring long-term stable operation, we recommend the THD or THB type, which uses mechanical anchoring to reduce maintenance.
Select based on production requirements:
For high-yield wells, we recommend the THB type (bottom anchoring), which offers high stability and resists loosening.
For medium- and low-yield wells, we recommend the THM or THC type, which offers better cost-effectiveness.
7. TH Tubing Pump Installation Method:
Assemble the pump barrel and tubing as a single unit and lower it into the well.
Connect the plunger and sucker rod assembly.
Lower the tubing to the designed depth at the bottom of the well.
Adjust the pumping unit stroke and pump efficiency.
Start normal production and monitor operation.
Unlike insertion pumps, TH tubing pumps require the entire tubing to be removed for maintenance or replacement.
8. Technical Parameters:
Tubing Specifications: 2 3/8 in., 2 7/8 in., 3 1/2 in., 4 1/2 in.
Pump Barrel Length: 6.1 m–9.14 m (20 ft–30 ft)
Plunger Stroke: 0.305 m (1 ft) increments
Pump Diameter Range: 20–175, 25–225, 30–275, 40–375
Valve Material: Alloy Steel, Nickel-Based Alloy, Customizable
FAQ:
Q: What is an APT (Aluminum Pipe Rod Pump)?
A: An APT (Aluminum Pipe Rod Pump) is a highly efficient underground oil production equipment designed for low- to medium-yield wells.
Q: What are the core advantages of an APT (Aluminum Pipe Rod Pump)?
A: The rod tubing pump (API) features chrome-plated/tungsten carbide plungers, offering a wear life of over 5,000 hours and reducing maintenance frequency.
Q: Can the API rod tubing pump support complex well conditions?
A: The API rod tubing pump (API) is available in alloy steel/stainless steel materials and customizable with corrosion-resistant coatings to accommodate wells with high sand content and high salinity.
Q: Are there any installation restrictions?
A: The API rod tubing pump (API) supports custom pump diameters from 38 to 95 mm to accommodate various wellbore structures.
Q: How can I extend the service life of the API rod tubing pump (API)?
A: Regularly monitor the sinking level to avoid dry grinding. Using sand control screens can improve the stability of the rod tubing pump's operation.
Contact Us:
We not only provide complete TH-type tubing pumps, but also offer individual replacement of wear parts such as valve balls, valve seats, plungers, and pump barrels. This helps customers reduce maintenance costs, shorten well downtime, and ensure continuous and stable oil production.

